Table of Contents
Introduction
The Qianbei Power Station, located in Chengguan Town, Jinsha, Bijie, Guizhou, China, stands as a testament to China’s ambitious energy infrastructure development.
As part of the Global Coal Plant Tracker, this operating power station boasts a capacity of at least 1200 megawatts (MW), contributing significantly to the region’s energy needs.
This article delves into the project’s location, details, background, ownership, and its significance within the broader context of China’s energy sector.
Location
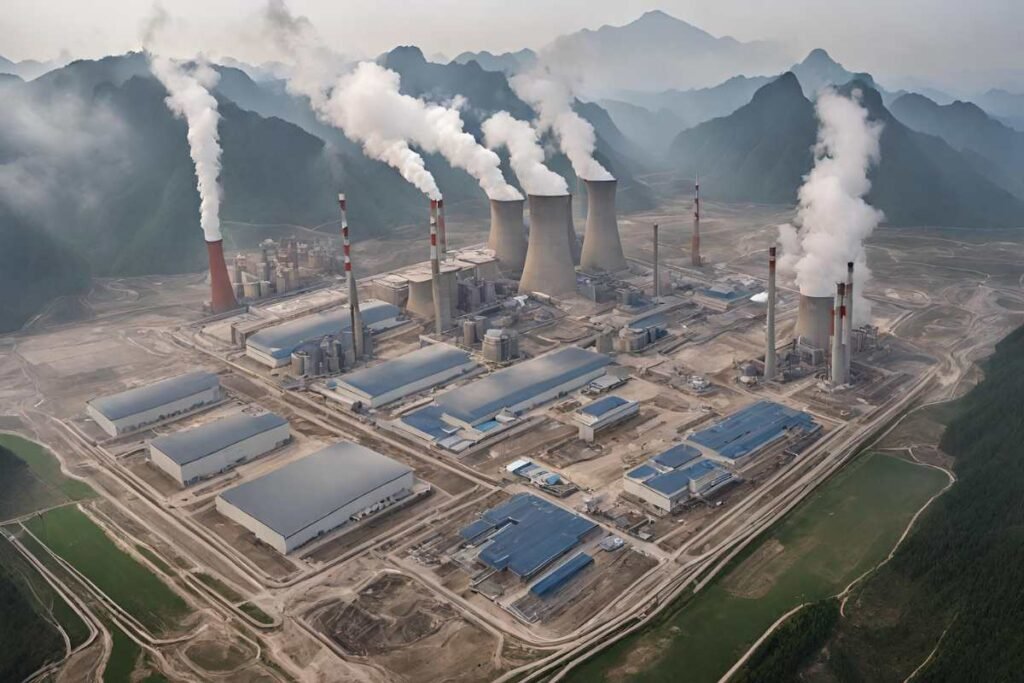

Nestled in the vibrant heart of Guizhou Province, the Qianbei Power Station assumes a pivotal role in the vast landscape of China’s energy infrastructure.
Positioned precisely at the coordinates of 27.475407 latitude and 106.258171 longitude, this power station isn’t just a mere point on the map; it stands as a cornerstone in the local and regional electricity grid.
Its strategic location allows it to effectively distribute power, ensuring stable energy supply to both nearby communities and more distant areas.
By bolstering the region’s power network, the Qianbei Power Station plays an indispensable role in supporting economic growth and enhancing the quality of life for countless individuals.
Project Details
The Qianbei Power Station, a significant infrastructure project, encompasses multiple units, each serving a distinct purpose in electricity generation. The construction of this power station was phased to ensure a gradual increase in its capacity and efficiency.
The first phase of the project, a cornerstone in the station’s development, featured four units, each boasting a capacity of 125 MW.
These units, which came online progressively between 1998 and 2000, marked the initial step towards fulfilling the region’s growing energy needs.
Fueled by bituminous coal, these units utilized subcritical technology to generate electricity, a method that, while effective, has been surpassed by more efficient technologies in recent years.
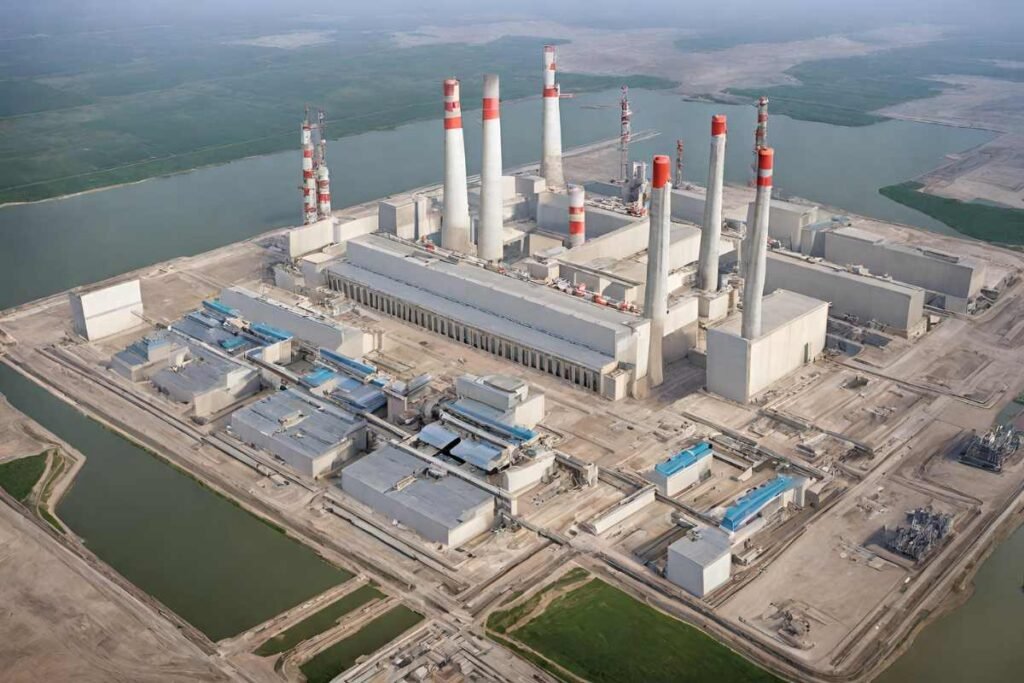

Despite their pivotal role, these units were retired in 2014, making way for advancement and modernization.
The project’s second phase was embarked upon with an eye towards amplifying the power station’s output significantly.
This phase introduced four additional units, each with a substantially higher capacity of 300 MW, designed to meet the escalating demand for electricity. Like their predecessors, these units were coal-fired and operated using subcritical technology.
However, their enhanced capacity represented a significant leap in the power station’s ability to provide for the energy needs of the area.
Completed between 2003 and 2004, this phase not only expanded the Qianbei Power Station’s capabilities but also underscored the ongoing efforts to bolster the regional power infrastructure to support economic growth and development.
Background on Project
The Qianbei Power Station’s journey is a vivid illustration of the evolving landscape of China’s energy policies and the progression of its infrastructure development.
When the decision was made to retire the first phase units in 2014, it was a clear reflection of the urgent need to modernize and optimize the country’s energy portfolio to meet future demands.
This pivotal move was in line with the government’s “shutting down small to build big” policy, which marked a significant strategic shift towards adopting more efficient and environmentally friendly methods of energy generation.
This policy aimed not only to enhance the energy sector’s capacity and efficiency but also to reduce the environmental impact of energy production.
Following this strategic adjustment, the expansion project, initially referred to as Qianbei-2 Power Station and later renamed to Jinsha Chayuan Power Station, was developed as a direct response to the region’s escalating energy demands and the rapid technological advancements in power generation.
This project was envisioned to not only expand the capacity to meet growing demands but also to incorporate advanced technologies that would improve efficiency and reduce emissions.
The development of the Jinsha Chayuan Power Station signified a step forward in China’s commitment to sustainable energy development and its efforts to balance economic growth with environmental preservation.
This story of adaptation and advancement underscores the dynamic nature of China’s approach to energy policy and infrastructure development, highlighting the country’s ongoing quest for innovation and sustainability in the energy sector.
Ownership
Originally under the ownership of Guizhou West Electric Power Co Ltd, a pivotal change occurred for the Qianbei Power Station when it became part of a larger narrative in China’s energy sector.
This shift resulted from a strategic merger between two major entities in the power industry: China Power Investment Corporation (CPI) and State Nuclear Power Technology Corporation (SNPTC) in July 2015.

The fusion of these corporations led to the birth of the State Power Investment Corporation, a powerhouse in the energy sector, thereby consolidating the station’s ownership under the umbrella of one of China’s five largest state-owned electricity producers.
This transition was far from just a change in ownership. It underscored the Chinese government’s unwavering commitment to streamlining and optimizing the energy sector.
By bringing the Qianbei Power Station under the State Power Investment Corporation’s wing, the move was emblematic of a larger strategy aimed at enhancing the efficiency and governance of the national energy policy.
This repositioning not only solidified the station’s role in China’s energy landscape but also highlighted its significance within the broader framework of national energy policy and governance, setting a precedent for future endeavors in the energy sector’s evolution.
Significance and Future Outlook
The Qianbei Power Station stands as a crucial pillar in China’s energy landscape, playing a significant role in powering regional development, driving economic growth, and ensuring energy security for the nation.
As a key player in China’s vast energy infrastructure, the station’s operations are central to meeting the country’s burgeoning energy demands.
However, its heavy reliance on coal-fired technology raises pressing concerns regarding environmental sustainability and the escalating problem of carbon emissions, which are at odds with global efforts to combat climate change.

Acknowledging these critical challenges, China has been proactive in reevaluating its energy strategies, with a strong push towards diversifying its energy portfolio.
The focus has shifted towards harnessing renewable energy sources, including the vast potential of solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, marking a pivotal transition in the country’s journey towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy future.
This strategic pivot not only reflects China’s commitment to reducing its carbon footprint but also aligns with international environmental objectives.
The gradual shift towards cleaner, renewable energy sources presents a spectrum of opportunities and challenges for the Qianbei Power Station and other coal-dependent facilities throughout China.
It opens avenues for modernization and innovation, allowing these establishments to evolve and adapt in an increasingly eco-conscious world.
However, it also signifies a period of transformation that requires significant investment, technological advancement, and policy support to ensure a smooth transition from traditional coal-fired methods to greener alternatives.
As China continues to pursue its ambitious goals for energy diversification and sustainability, the future of the Qianbei Power Station and its counterparts remains at a crossroads.
The journey toward cleaner energy is fraught with challenges but is also ripe with opportunities for growth, innovation, and leadership in the global effort to ensure a sustainable energy future.
Conclusion
The Qianbei Power Station serves as a microcosm of China’s energy transition journey, encapsulating the country’s relentless pursuit of progress amidst the challenges of balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability.
Situated in Guizhou Province, this coal-fired power station has played a crucial role in meeting regional energy demands, contributing significantly to economic development and energy security.
However, its reliance on coal-fired technology underscores pressing environmental concerns, prompting China to pivot towards renewable energy sources to mitigate carbon emissions and align with global sustainability objectives.
As China navigates this transition, the Qianbei Power Station stands at a crossroads, poised to embrace innovation and adaptation in the pursuit of a greener, more sustainable energy future.
By embracing renewable energy sources and fostering technological innovation, the Qianbei Power Station can transcend its reliance on coal and emerge as a beacon of sustainable energy development, not only for China but for the world at large.
FAQs
What is the capacity of the Qianbei Power Station?
The Qianbei Power Station boasts a capacity of at least 1200 megawatts (MW), contributing significantly to the region’s energy needs.
When were the first phase units of the power station operational?
The first phase units of the Qianbei Power Station came online progressively between 1998 and 2000.
What type of technology was used in the first phase units?
The first phase units utilized subcritical technology for electricity generation.
When were the second phase units completed?
The second phase units of the Qianbei Power Station were completed between 2003 and 2004.
What was the capacity of the second phase units?
The second phase units had a substantially higher capacity of 300 MW each, marking a significant leap in the power station’s ability to provide for the energy needs of the area.
Why were the first phase units retired in 2014?
The retirement of the first phase units in 2014 matched China’s strategy to modernize its energy sector. This action, under the “shut down small, build big” policy, sought to embrace more efficient and eco-friendly energy generation methods.
What was the purpose of the Qianbei-2 Power Station expansion project?
The expansion project aimed to meet the region’s escalating energy demands and incorporate advanced technologies to improve efficiency and reduce emissions.
What prompted the transition in ownership of the Qianbei Power Station?
The ownership transitioned after CPI and SNPTC merged in July 2015, placing the station under State Power Investment Corporation’s control.


